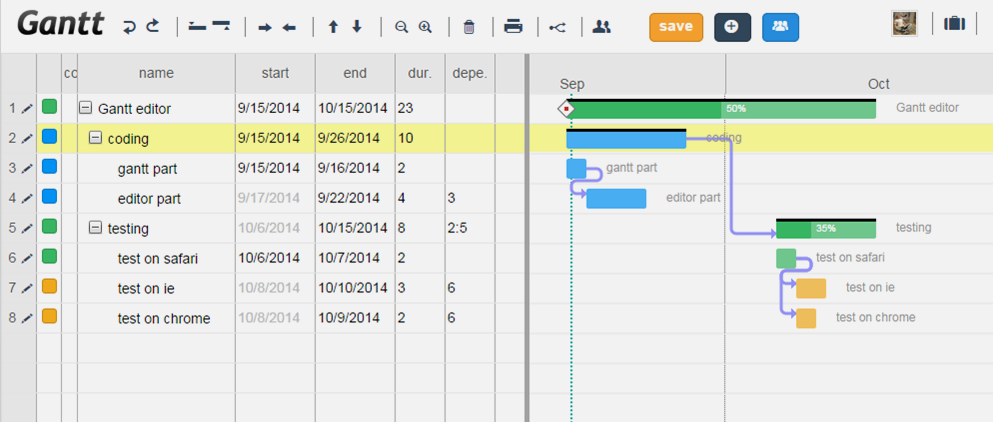
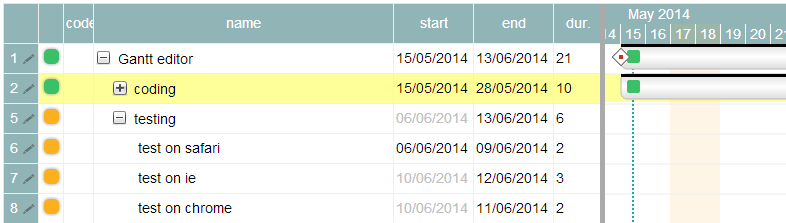
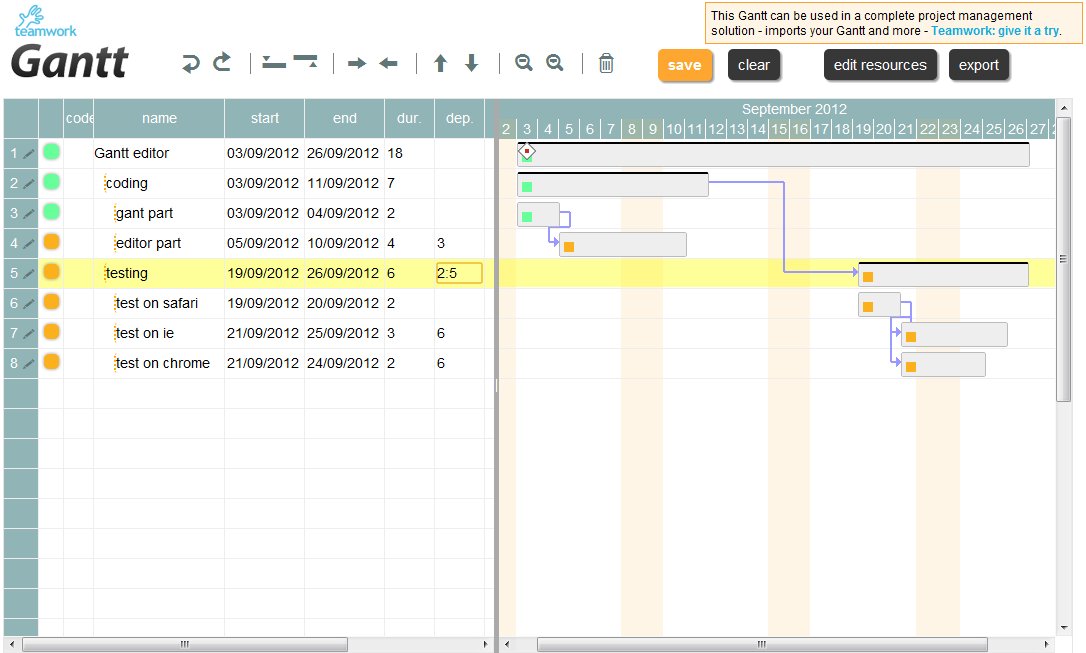
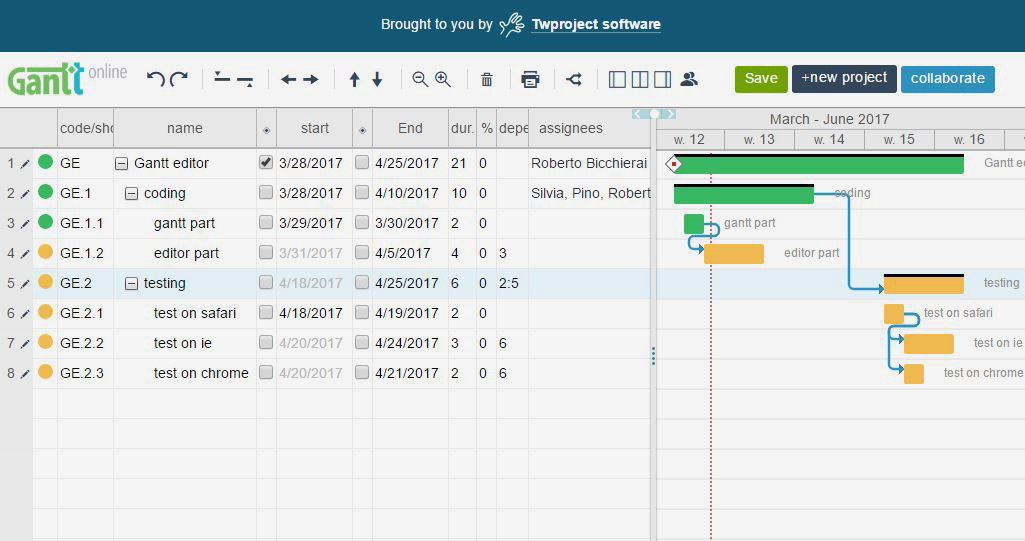
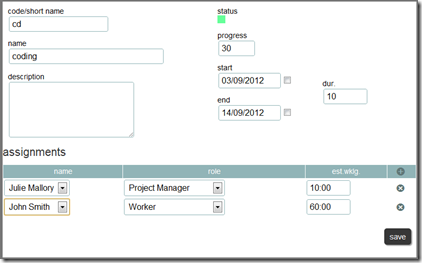
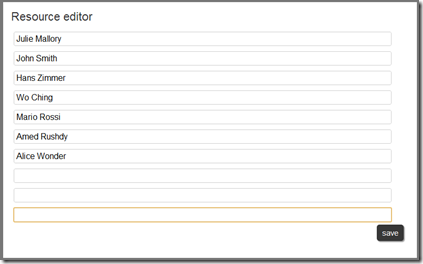
As promised in my last post, here I will try to explain how to use our jQuery Gantt editor, how it works and how to customize it for your needs.
First let me list its key features:
- jQuery based
- MIT licensed: you can reuse it everywhere
- json import-export
- internationalizable
- manage task statuses –> sort of workflow handling
- manage dependecies
- manage assignements (resources, roles, efforts)
- server synchronization ready
- full undo-redo support
- cross browser (at least for recent versions)
Source codes are available on GitHub here: https://github.com/robicch/jQueryGantt
In order to better understand this component I will introduce some concepts below.
Genesis
This editor has been created mainly as part of our project management solution, Twproject.
During the development we always kept in mind creating an open-source reusable “component”, while the focus was integration with Twproject. This constraint gave us the opportunity to extend the standard Gantt behaviour by introducing key features like task’s statuses, or time buffers for parent tasks.
This is not the right place to discuss how these features make project modelling and management more flexible and closer to the real world: if you want go deeper have a look at Twproject user guide.
If Twproject’s model influenced the behavior of the editor, the environment where Twproject lives (Java Jsp Html5 jQuery internationalized server side multi-db cross-operating-system etc.) influenced the packaging and the libraries of our editor; this is the reason for so many dependencies.
Despite this facts, our Gantt editor can be easily customized and extended as Javascript component.
Main concepts
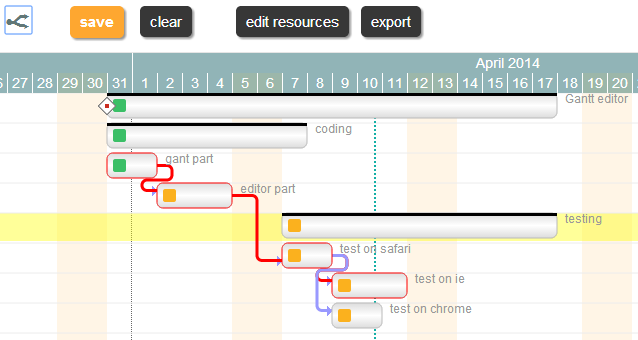
While a Gantt viewer (hence read-only) can be easily packed as a single component, a Gantt editor is a way more complicated object; so I prefer to think of it as jQuery application and not just as a plugin.
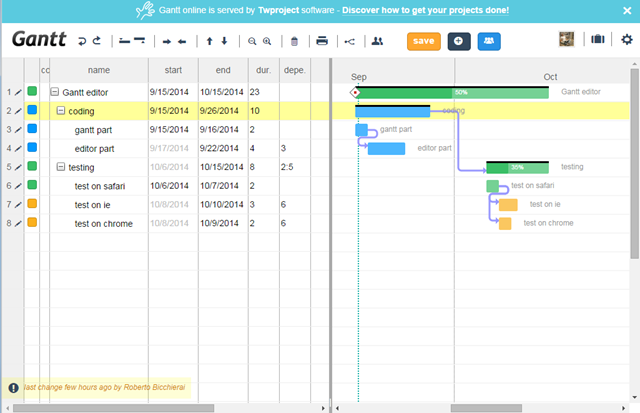
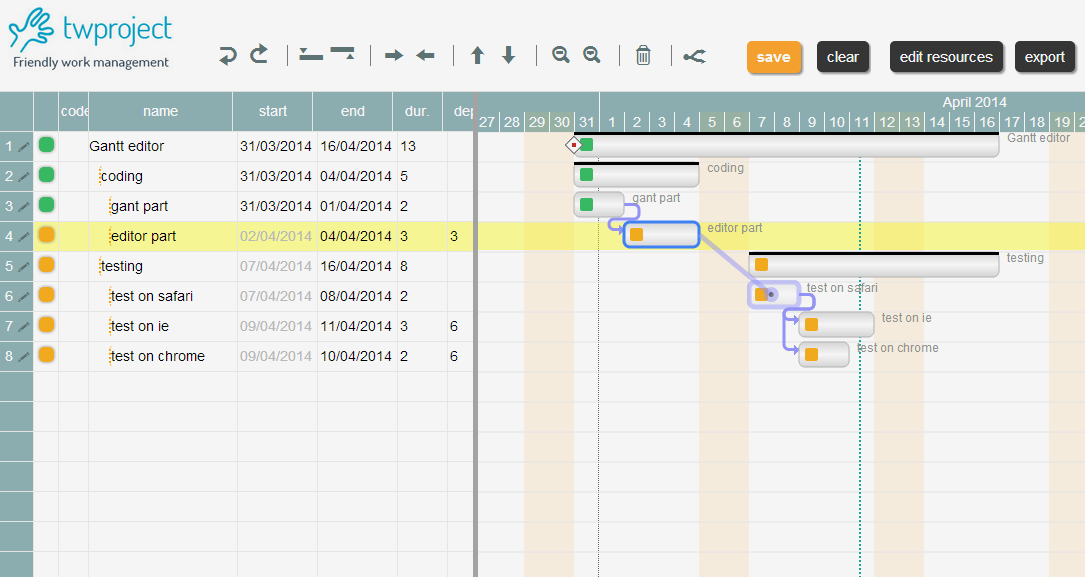
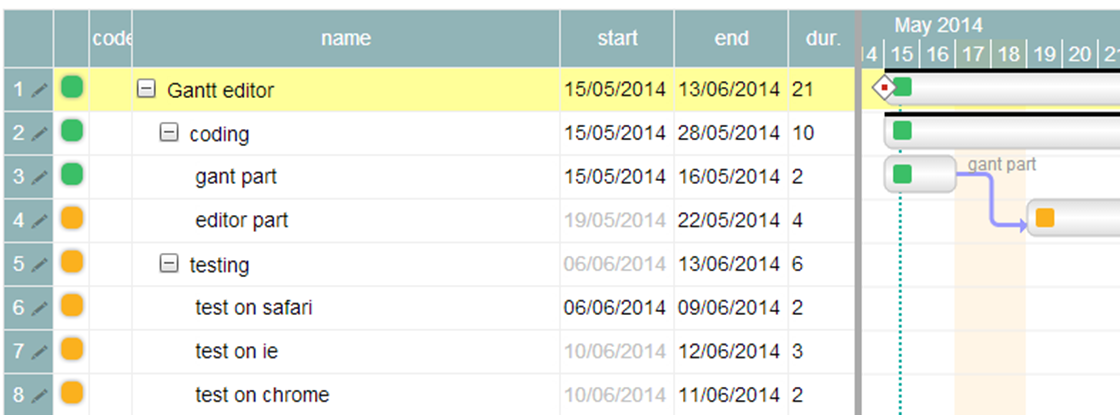
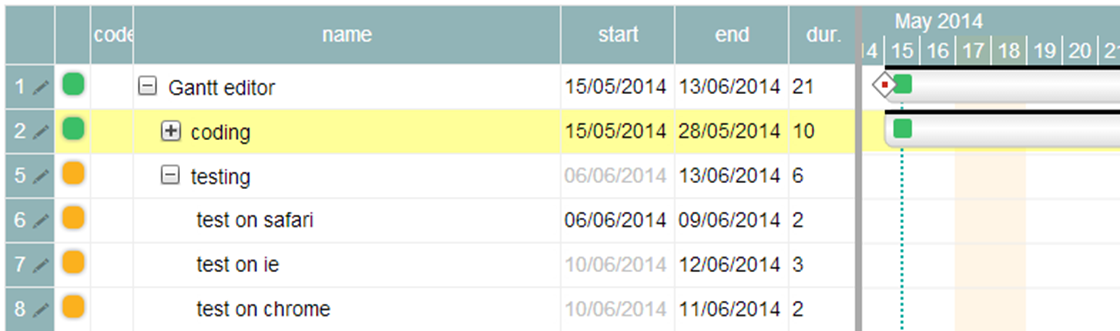
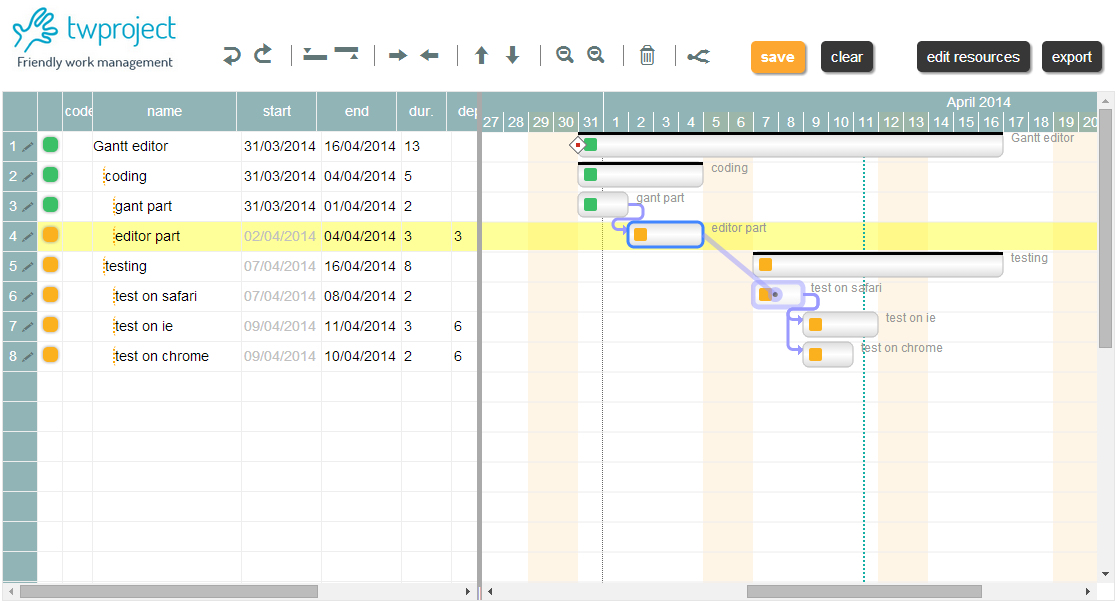
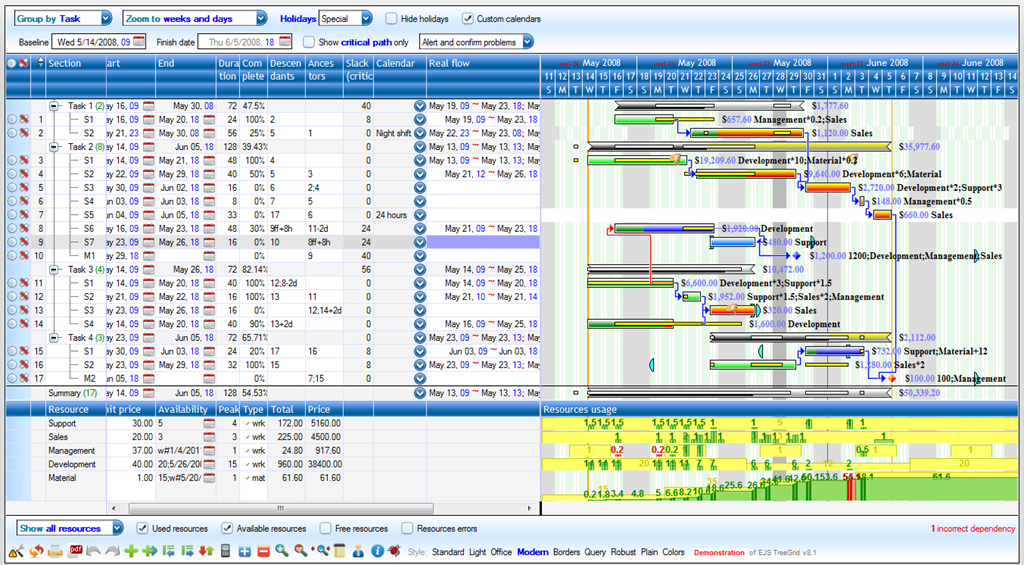
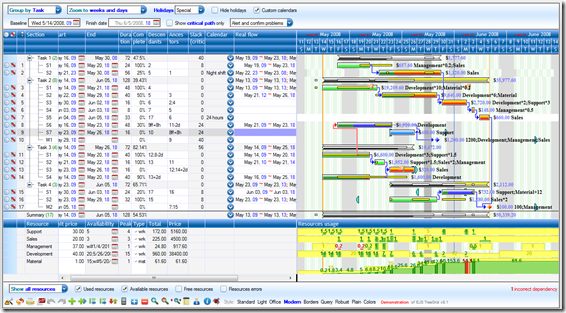
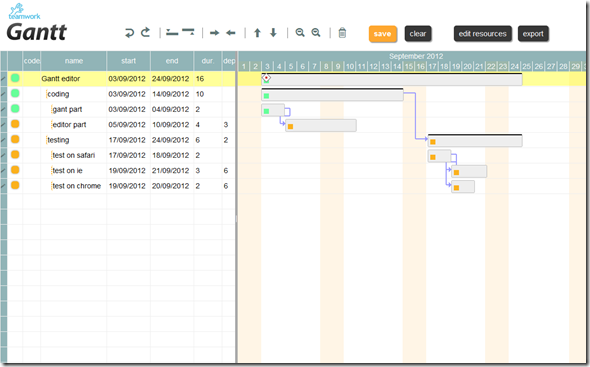
Actually our Gantt editor is composed by three main sub parts/editors: the grid editor on the left, the Gantt editor on the right, and the detailed task editor in popup; actually the popup editor is used also for resources and assignments.
The goal of our editor is to generate a json file representing the full project state that could be sent to a server to store it. During editing there is no interaction with the server.
The distributed version uses local storage to save the project status, but examples of server calls are available in the source code.
How to use it
Download the component source code here, unzip the file: the “gantt.html” is already a working Gantt editor. If you open “gantt.html” with your preferred html editor: the source contains some comments so it should be readable  .
.
To play with the code use Firefox with Firebug plugin installed or Chrome (as I do).
In the code first we defined a global variable for accessing the editor, called “ge”.
In your browser try to change something on the gantt and then from your js debugger execute
ge.saveProject()
This method returns the project in form of a json object. In the demo page we use local storage for saving the project (or a textarea if local storage is not available), but in a real environment you probably will need to send data to a server. I left a commented code for ajax communication with the server.
In order to load a project you must obviously supply a json object in the same format that has been saved on the server:
ge.loadProject( <em>[yourJsonProject] </em>)
The same json object can be used both ways: load or save, and in consequence client-to-server or server-to-client.
Project data structure
This is a project json object structure:
{
tasks:[…]
resources: […]
roles: […]
… more
}
here tasks, resources and roles are arrays.
As it easy to guess, the “tasks” array contains a list of task in the Gantt, and this is the most relevant data to manage.
“Resources” and “roles” will be easy to understand by looking first to a task element in the “tasks” array:
{
"id":"tmp_fk1345562123031",
"name":"approval",
"code":"APP",
"level":2,
"status":"STATUS_SUSPENDED",
"start":1348696800000,
"duration":10,
"end":1349906399999,
"startIsMilestone":false,
"endIsMilestone":false,
"assigs":[…],
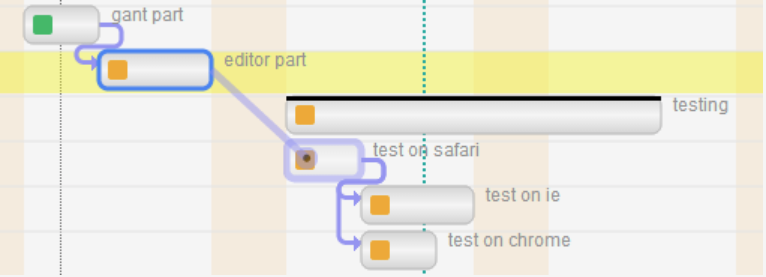
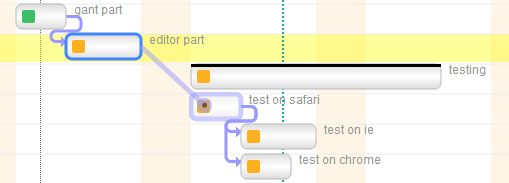
"depends":"7:3,8",
"description":"Approval of testing",
"progress":20
}
First important consideration: the order of tasks in the array is the same of the editor. The index of the array is used as reference for dependencies.
Attributes like name, code and description require no explanation, but some do:
mainly assignments are structured for carrying server-side data:
- resourceId: is the unique id for the resource. Refers to the “resources” array
- id: is the unique identifier of this assignment
- roleId: is the unique identifier of this assignment. Refers to the “roles” array
- effort: is the estimated effort in milliseconds
The “resources” array contains elements in the following form:
{
"id":"tmp_1",
"name":"Resource 1"
}
The “roles” array contains elements in the following form:
{
"id":"tmp_1",
"name":"Project Manager"
}
You must remember that this editor is the client part of something that manages persistence, alerts, interaction with other systems server-side; so we have to handle a few more attributes:
deletedTaskIds:[…]
selectedRow: 7
canWrite: true
canWriteOnParent: true
minEditableDate:1349906300000
maxEditableDate:3499063999999
where
- deletedTaskIds: is an array containing the ids of the tasks removed client side. Only tasks with a “real” id will be notified to the server (so not those starting with “tmp_”), locally generated ones will be removed silently.
- selectedRow: is the line currently in edit
- canWrite: is a boolean stating if you have permission to write/change/create/delete tasks on this project or not. Set it to true for a basic usage.
- canWriteOnParent: this is a little bit obscure. It is used in case you are editing only a small part of a complex project. For instance you are a PM of sub-task but not of the top-project: maybe some changes you made on dates may affect the top-project schedule.
Setting this boolean to false you will stop propagation to top project/s. Set it to true for a basic usage.
- minEditableDate, maxEditableDate: are the boundaries used in case you can’t write on parent
Here is an example a the project json object:
{
"tasks":[
{
"id":"tmp_fk1345624806538",
"name":"Gantt editor ",
"code":"",
"level":0,
"status":"STATUS_ACTIVE",
"start":1346623200000,
"duration":5,
"end":1347055199999,
"startIsMilestone":false,
"endIsMilestone":false,
"assigs":[
{
"resourceId":"tmp_3",
"id":"tmp_1345625008213",
"roleId":"tmp_1",
"effort":7200000
}
],
"depends":"",
"description":"",
"progress":0
},
{
"id":"tmp_fk1345624806539",
"name":"phase 1",
"code":"",
"level":1,
"status":"STATUS_ACTIVE",
"start":1346623200000,
"duration":2,
"end":1346795999999,
"startIsMilestone":false,
"endIsMilestone":false,
"assigs":[
{
"resourceId":"tmp_1",
"id":"tmp_1345624980735",
"roleId":"tmp_1",
"effort":36000000
}
],
"depends":"",
"description":"",
"progress":0
},
{
"id":"tmp_fk1345624789530",
"name":"phase 2",
"code":"",
"level":1,
"status":"STATUS_SUSPENDED",
"start":1346796000000,
"duration":3,
"end":1347055199999,
"startIsMilestone":false,
"endIsMilestone":false,
"assigs":[
{
"resourceId":"tmp_2",
"id":"tmp_1345624993405",
"roleId":"tmp_2",
"effort":36000000
}
],
"depends":"2",
"description":"",
"progress":0
}
],
"resources":[
{
"id":"tmp_1",
"name":"Resource 1"
},
{
"id":"tmp_2",
"name":"Resource 2"
},
{
"id":"tmp_3",
"name":"Resource 3"
}
],"roles":[
{
"id":"tmp_1",
"name":"Project Manager"
},
{
"id":"tmp_2",
"name":"Worker"
}
],
"canWrite":true,
"canWriteOnParent":true,
"selectedRow":0,
"deletedTaskIds":[],
}
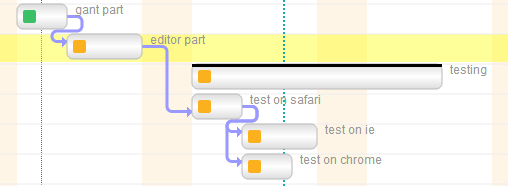
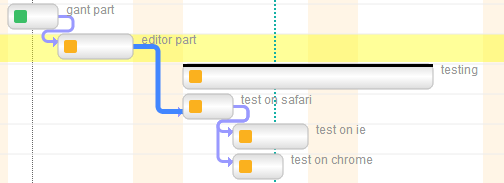
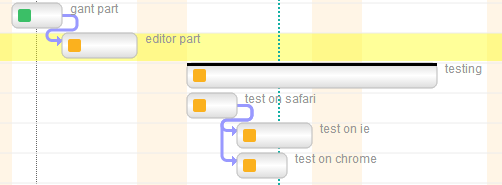
Status transition rules (aka project workflow)
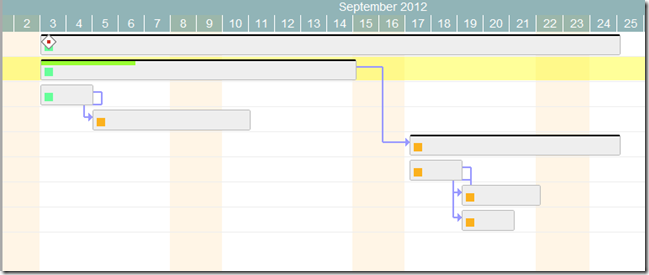
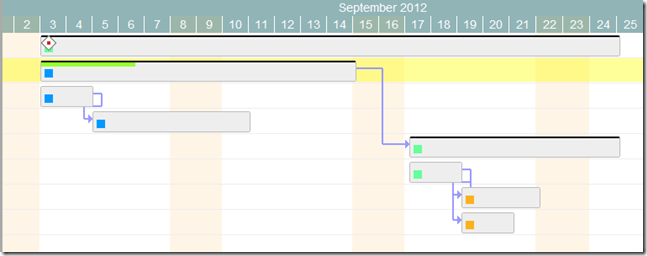
Task statuses are a key feature of Twproject, and our Gantt editor supports them in full.
Use the demo page and try to close some tasks (change status to “completed”); you will see how dependent tasks/children will change their status according to the following rules:
- any status-> STATUS_DONE: may activate dependent tasks, both suspended and undefined. Will set to done all descendants.
- STATUS_FAILED -> STATUS_DONE: do nothing if not forced by hand.
- STATUS_UNDEFINED -> STATUS_ACTIVE: all children become active, if they have no dependencies.
- STATUS_SUSPENDED -> STATUS_ACTIVE : sets to active all children and their descendants that have no inhibiting dependencies.
- STATUS_DONE -> STATUS_ACTIVE: all those that have dependencies must be set to suspended.
- STATUS_FAILED -> STATUS_ACTIVE: nothing happens: child statuses must be reset by hand.
- any status-> STATUS_SUSPENDED: all active children and their active descendants become suspended. when not failed or forced
- any status-> STATUS_UNDEFINED: all active children and their active descendants become suspended. when not failed or forced.
- any status-> STATUS_FAILED: children and dependants are set to failed.
A basic minimal implementation
The demo example is quite simple and commented, it should the right point to start.
Here I’ll sum-up what you’ll need to use our Gantt editor in your application:
first include javascript dependencies
<script src="/jquery/1.7/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="/jquery-ui.min.js"></script>
<script src="libs/jquery.livequery.min.js"></script>
<script src="libs/jquery.timers.js"></script>
<script src="libs/platform.js"></script>
<script src="libs/date.js"></script>
<script src="libs/i18nJs.js"></script>
<script src="libs/dateField/jquery.dateField.js"></script>
<script src="libs/JST/jquery.JST.js"></script>
<script src="ganttUtilities.js"></script>
<script src="ganttTask.js"></script>
<script src="ganttDrawer.js"></script>
<script src="ganttGridEditor.js"></script>
<script src="ganttMaster.js"></script>
then some css
<link rel=stylesheet href="platform.css" type="text/css">
<link rel=stylesheet href="libs/dateField/jquery.dateField.css" type="text/css">
<link rel=stylesheet href="gantt.css" type="text/css">
then you need a div where to place the editor, something like:
<div id="workSpace" style="padding:0px; overflow-y:auto; overflow-x:hidden; border:1px solid #e5e5e5; position:relative; margin:0 5px; width:1024px; height:800px;"></div>
now create the Gant editor and bind it to your div
var ge = new GanttMaster();
ge.init($("#workSpace"));
your editor its ready to use.
If you want to know how our Gantt editor works, go in depth by reading next chapter…
How it is built
Environment first!
Libraries
Our Gantt editor is based on jQuery and use some jQuery UI components like draggable, sortable etc.
Other jQuery related libraries are used here like livequery and timers.
For data selection I used one of my components (I have not yet published it but I will…; anyway its included here):
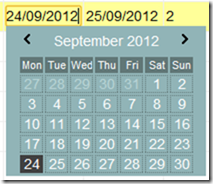
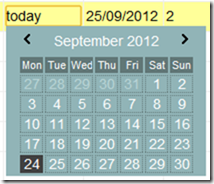
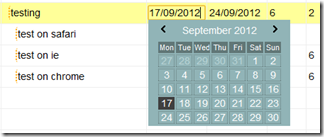
It supports date shortcuts like “t” (today), “y” (yesterday), “lm” (last month), “lq” (last quarter), “-4w” (4 week ago) and so on. See files on “/libs/dateField” folder for details. This component is MIT licensed so use it!
Another key component is a javascript template library called “JST” that I wrote some years ago and discussed in a previous post “Easy going JavaScript templates”.
It is used for creating editor side rows and Gantt task elements. The library is in “/libs/JST” folder; it is very powerful and I used it in several products.
Our Gantt editor uses extensively date computation and formatting.
I used Matt Kruse’s date library with some extensions for managing holidays in date computation and with some changes for more comprehensive support of Java date formats and internationalization.
Our Gantt editor supports internationalization, but only English is implemented. Have a look at “/libs/i18n.js” file. Here you will find all the internationalization defaults, including the definition of a sample holidays calendar.
The last library used is “/libs/platform.js” that is a sort of toolbox for input validation, feedback management, extension of js objects (String, Array, Date) for cross-browser compatibility and other tricks.
I’m not very proud of this library and I cleaned it up many times with the secret hope to remove it completely, but it is very tightly linked to our “historic” development environment; if I had to fork the Gantt from our platform it would become difficult to maintain.
Core objects
We have now arrived at the application’s core.
We divided the editor in three parts:
- the GridEditor object that manages the left part of the editor. Data editing is managed here.
- the Ganttalendar (sorry for the ugly name!) object that manages the right part of the editor with Gantt drawing, calendar scale, task date movement
- the GantMaster object that is responsible for the coordination of both sides, transactional management, event management and persistence.
Your code should “talk” only with this object.
These objects are in the gridEditor.js, gantDrawer.js and gantMaster.js files respectively.
The entities managed are: Task, Link, Resource, Role, Assignment, and are defined in ganttTask.js file.
Events
Once the Gantt Editor has been initialized
var ge = new GanttMaster();
ge.init($(“#workSpace”));
it binds some events on the DOM object, in this case the DIV “workspace”.
Events bound are:
refreshTasks.gantt: perform a redraw of all tasksrefreshTask.gantt: accepts a task as parameter. Redraw the passed task:deleteCurrentTask.gantt: delete the current selected taskaddAboveCurrentTask.gantt: add a task above the current ones. The task inserted will be a brother of the current oneaddBelowCurrentTask.gantt: add a task below the current ones. The task inserted will be a child of the current oneindentCurrentTask.gantt: the current task will become a child of the task aboveoutdentCurrentTask.gantt: the current task will become a brother of the task abovemoveUpCurrentTask.gantt: the current task (and its own children) will be moved upmoveDownCurrentTask.gantt: the current task (and its own children) will be moved downzoomPlus.gantt: restrict the time scale of the Gantt side (more detail)zoomMinus.gantt: enlarge the time scale of the Gantt side (less detail)undo.gantt: undo the last actions performedredo.gantt: redo last actions
A basic usage for triggering an event will look like:
$('#workSpace').trigger('zoomMinus.gantt');
When you perform an action in the project tree, the action could propagate along the tree. There are many constraints that must be respected like milestones, statuses, dependencies, boundaries and so on. Every constrain could make it impossible to complete the operation so we decided to wrap tree operations with a “transaction”; in case of constraint violation we rollback all the changes already done.
Events are transaction-safe, so you don’t need to worry about them.
Methods
The GanttMaster object exposes some useful methods you may need for your application.
Be careful: unlike events, methods exposed are “low-level”, so you are responsible for managing transactions correctly; transactions are not managed unless otherwise specified.
Here is a list of most important methods:
init (jQueryDomObject)
description: creates the Gantt editor, initializes project arrays, binds events.
jQueryDomObject: is a jQuery proxy for a DOM object tipically a <div> where you want to create the Gantt editor
return: nothing
createTask (id, name, code, level, start, duration)
description: creates a Task object. The task created is not added to project, just created
id: task id
name: task name
code: task code
level: task indentation level. Root task is 0 (zero)
start: the task start date in millisecond
duration: task duration in days
return: the task created
createResource (id, name)
description: creates a Resource object. The resource created is not added to resource list, just created
id: resource id
name: resource name
return: the resource created
addTask (task, row)
description: adds a task to the project at the specified row
task: a Task object
row: row where to add the object, zero based
return: the task added
loadProject(project)
description: loads a project on the editor. This method is transaction safe.
project: a project in json format as above defined in “Project Data Format” section.
return: nothing
saveProject()
description: gets the project in json format as above defined in “Project Data Format” section
return: the json object
loadTasks(tasks,row)
description: adds tasks to the current project from the specified row on
tasks: an array of Task object
row: row where to start adding tasks, zero based
return: nothing
getTask(taskId)
description: retrieves a task by id
tasksId: the id of the task you want
return: a Task object
getResource(resourceId)
description: retrieves a resource by id
respurceId: the id of the resource you want
return: a Resource object
changeTaskDates (task, start, end)
description: changes scheduling for a task in the project
task: task you want to change
start: the task start date in millisecond
end: task end in milliseconds
return: true if changing was performed, false if changes required are invalid. Error codes are set on current transaction.
moveTask (task,newStart)
description: moves a task to a new starting date
task: task you want to move
start: the task start date in millisecond
return: true if changing was performed, false if changes required are invalid. Error codes are set on current transaction.
updateLinks(task)
description: updates project link structure as defined in “task.depends” property
task: task you want to change
return: true if changing was performed, false if changes required are invalid. Error codes are set on current transaction.
taskIsChanged ()
description: notifies GanttMaster that a task has been changed and enqueues a request for redrawing both sides. Redraw is executed asynchronously and only once after 50 milliseconds
return: nothing
redraw()
description: redraw both sides. Redraw is executed immediately
return: nothing
reset()
description: starts a new project and empties both sides
return: nothing
showTaskEditor(taskId)
desciption: shows the complete task editor in popup
taskId: the id of the task you want to edit
return: nothing
undo()
description: undoes the last operation performed. There is no limit to the number of operations (the limit is just the memory of your browser)
return: nothing
redo()
description: redoes last operation undo-ed
return: nothing
beginTransaction()
description: saves the current state of the project in memory. Transactions cannot be nested
return: nothing
endTransaction()
description: closes the current transaction by making changes performed active. If there are errors set on the transaction, it rollbacks to previous state
return: true in case of successful commit, false if a rollback was performed
setErrorOnTransaction(errorMessage, task))
description: sets an error message related to a Task object in the current transaction. If no transaction is started the message is displayed on console instead.
errorMessage: a string containing the error message
task: the Task object that generates the error
return: nothing
Customization
The Gantt editor uses CSS so you can play customizing your Gantt editor look-and-feel.
Regarding internationalization, the question is a little bit complicated. As I’ve already said, actually only the English version is available.
The file “libs/i18n.js” is used for managing generic language/country specific data. There you can change the values for month names, day names, currency format, date format and some default message strings. Actually in our real environment (Twproject) this file is server-side generated in base of user’s language settings.
In the same file you can/must change the implementation of the method isHoliday(date) that is used for taking care of working days. The current implementation supports both fixed holydays (like Christmas) and mobile ones (like Easter), but you can refine the implementation for your needs.
Gantt specific string are set on GanttMaster.messages object, and by default its values are in English: you can implement you own language.
Recycling
There are lots of “tools” that can be reused; here is a list of some that I think may save a lot of time to developers:
JST: a javascript templating system, see here previous post “Easy going JavaScript templates”, but the version in Gantt is the updated ones (read until my last comment in the post linked!)
DateField: a jQuery calendar input component. No frills!
Date/Time: lots of functions that support multiple formats, relative dates, shortcuts etc. The changes from Matt Kruse’s date library should be really useful for Java developers, and in general my version is a little bit more complete, even if the original its great by itself!
Gridify: a jQuery component that transforms a <table> making columns resizable. See it at work on the left side of Gantt editor
Splittify: a jQuery component that creates a splitter in a specified dom element. Used for splitting the editor from the Gantt part
Transaction, undo-redo: the idea and the implementation is very basic, so it can be used in many contexts
Profiler: a helpful tool for monitoring your javascript code performance
Field validation: validation function for email, url, date, time, integer, double, currency etc.
Everything is MIT!
I’m not sure if anyone can be interested on this stuff so for the moment that’s all, but in case someone is interested I’ll be pleased to publish a new post about them.
Every feedback will be really appreciated.